[1] S45C (Carbon Steel for Machine Structural Use):
Water-Soluble Cutting Oil Cleaning Test Results
Test Method
Specimen
- Material: S45C (black scale), blast-treated by the requester
- Sise: 20mm×20mm×1.6mm
- Pre-treatment: Immersed in acetone and ultrasonically irradiated for 60 seconds
Contamination
- Contaminant: Water-soluble cutting oil, Part No. 821 (AZ Co., Ltd.) (Fig. 1)
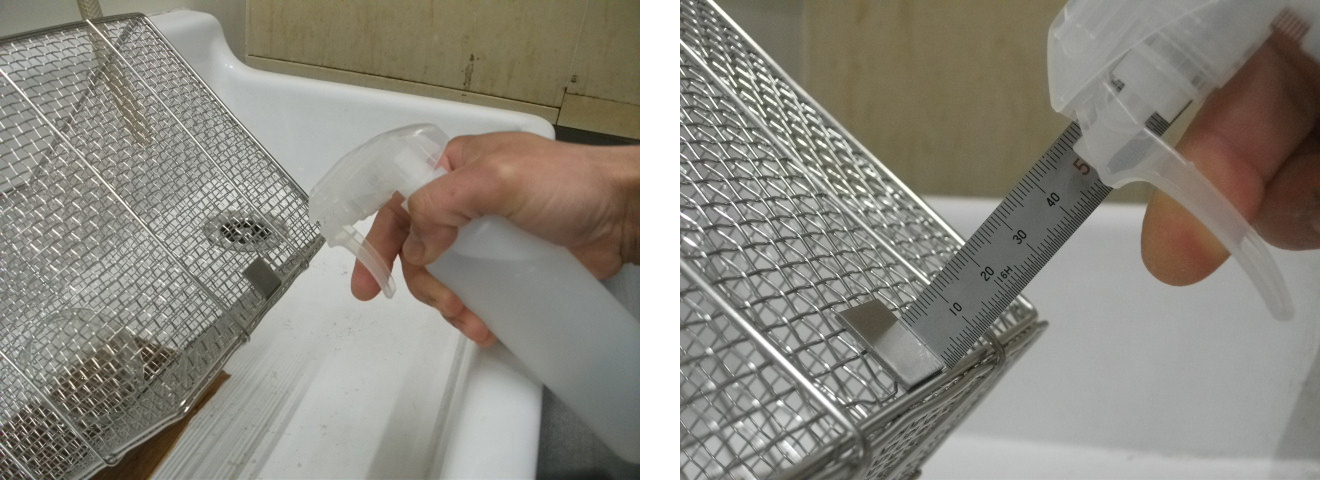
- Contamination method: 10 μL was dispensed onto the specimen center using a micropipette (Fig. 2)
Cleaning
- Cleaning solution: VB1000(Fig. 3)
Wipe test
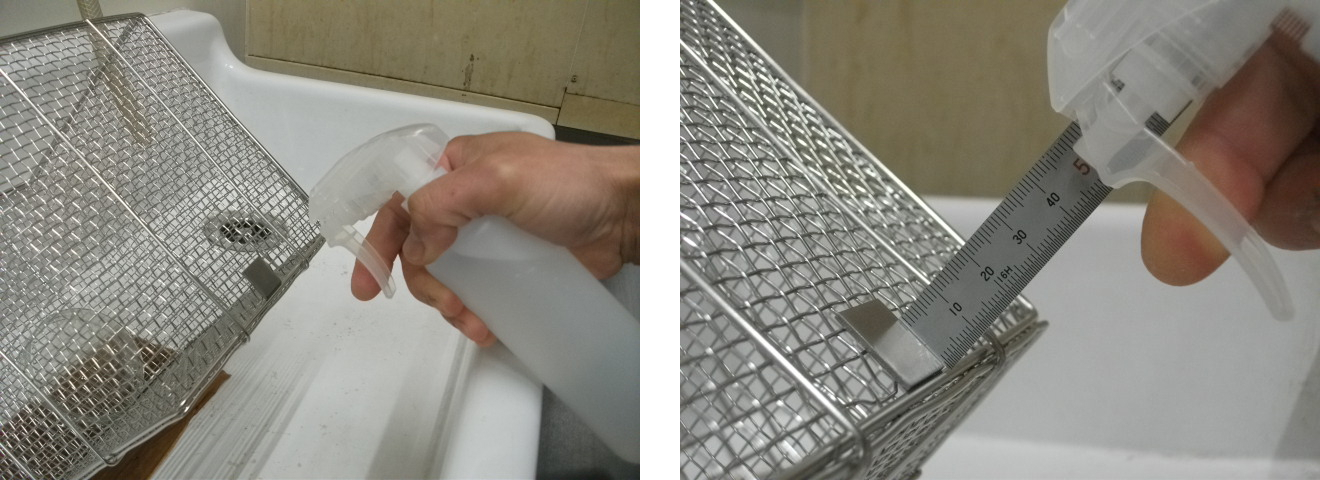
- On a specimen tilted ~45°, spray twice from 50 mm vertically above (Fig. 4), wait 10 seconds, then wipe once with a Kimwipe
Spray test
- On a specimen tilted ~45°, spray 10 times from 50 mm vertically above, wait 60 seconds, then rinse with tap water (70 mL/s for 10 seconds)
Immersion test
- Immerse in a dish filled with cleaning solution for 10 minutes, then rinse with tap water (70 mL/s for 10 seconds)
*Specimens, oil used, cleaning solution, and spray container were provided by the requester
Evaluation
Visual
- Visual observation of the specimen surface after cleaning
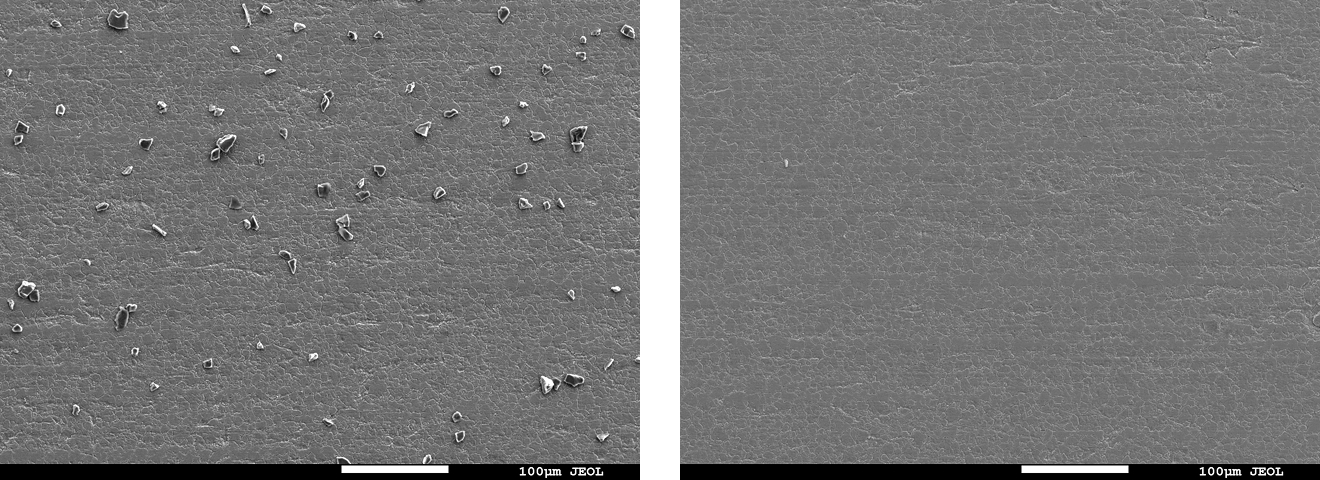
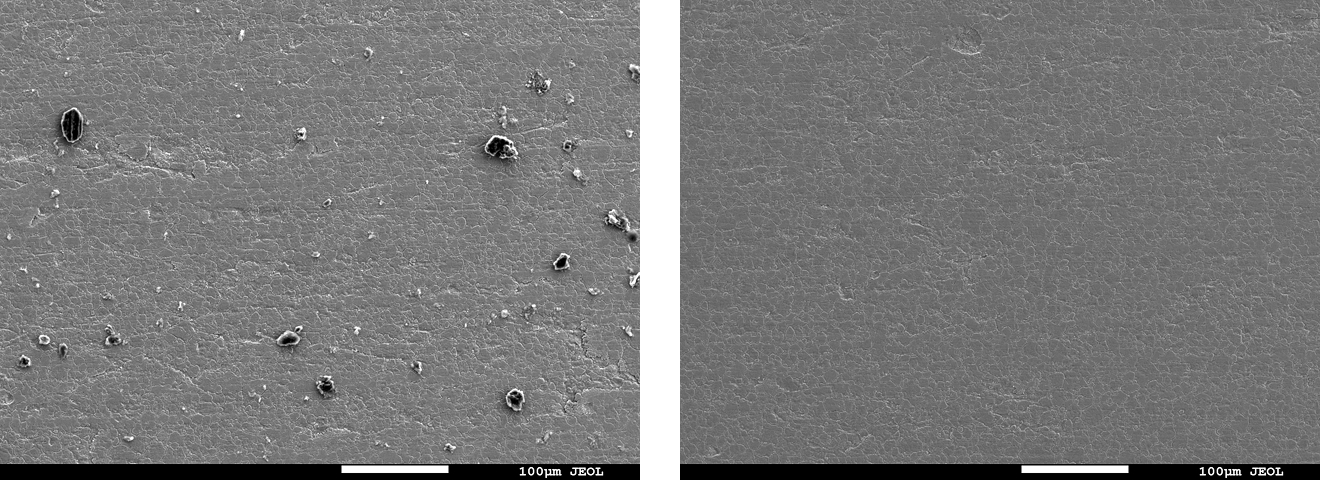
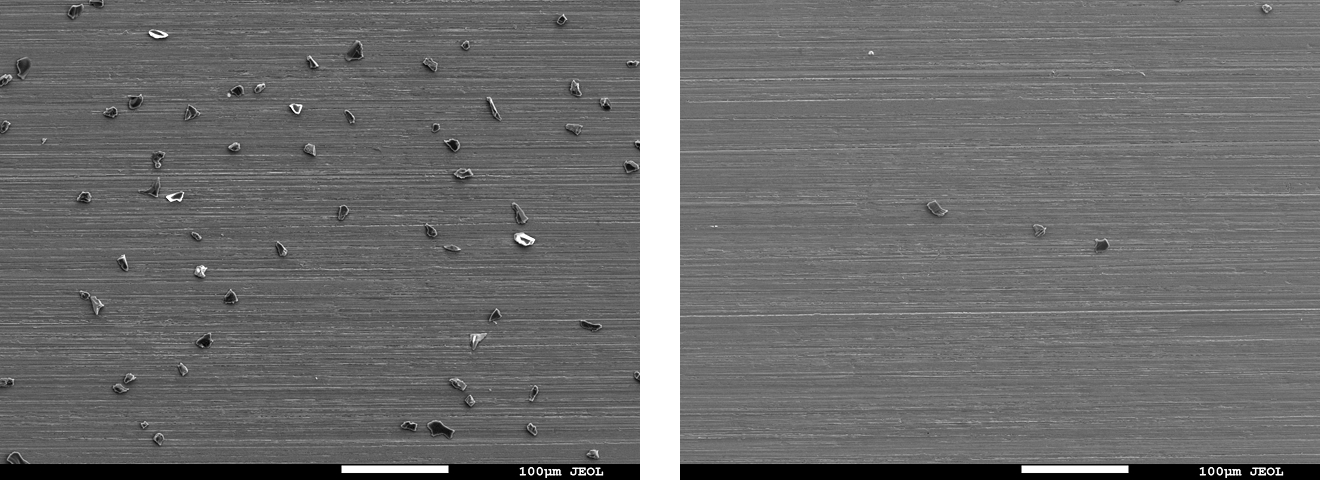
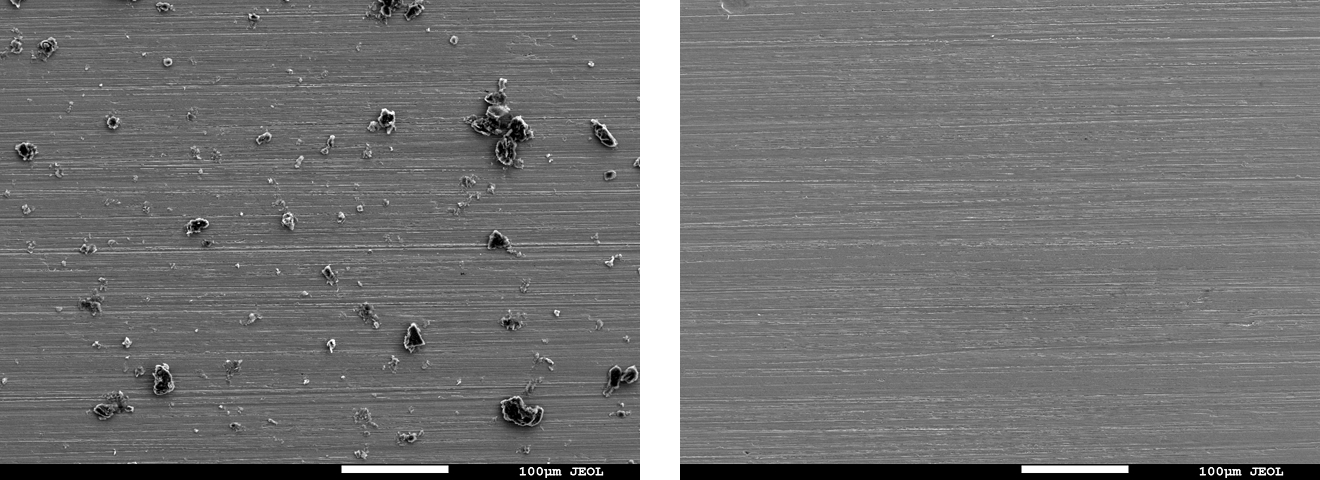
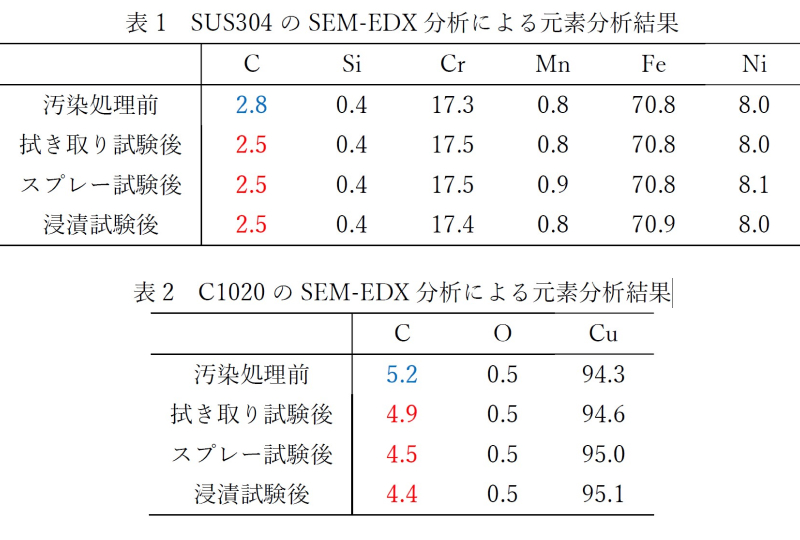
SEM observation and SEM-EDX analysis
- Instrument: Analytical FE-SEM JSM-7900F (JEOL Ltd.)
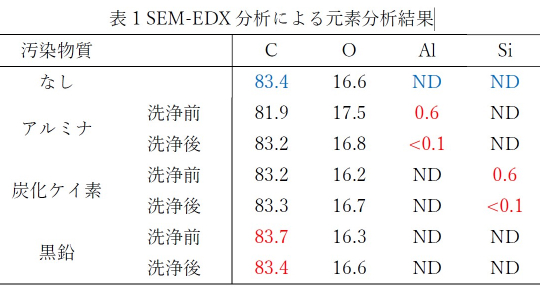
- Method: Compare carbon concentration after cleaning with the pre-contamination specimen
Results
Visual
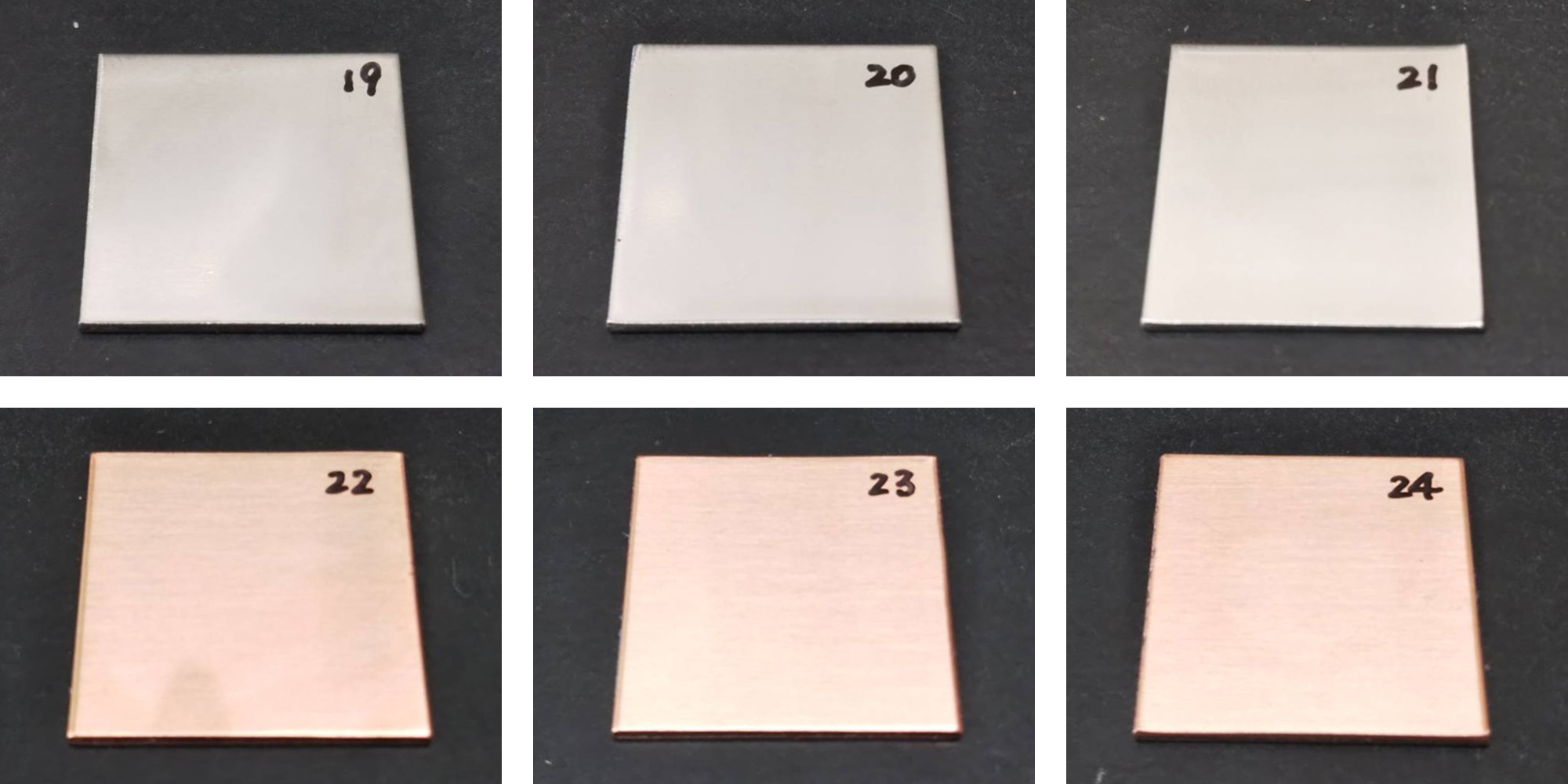
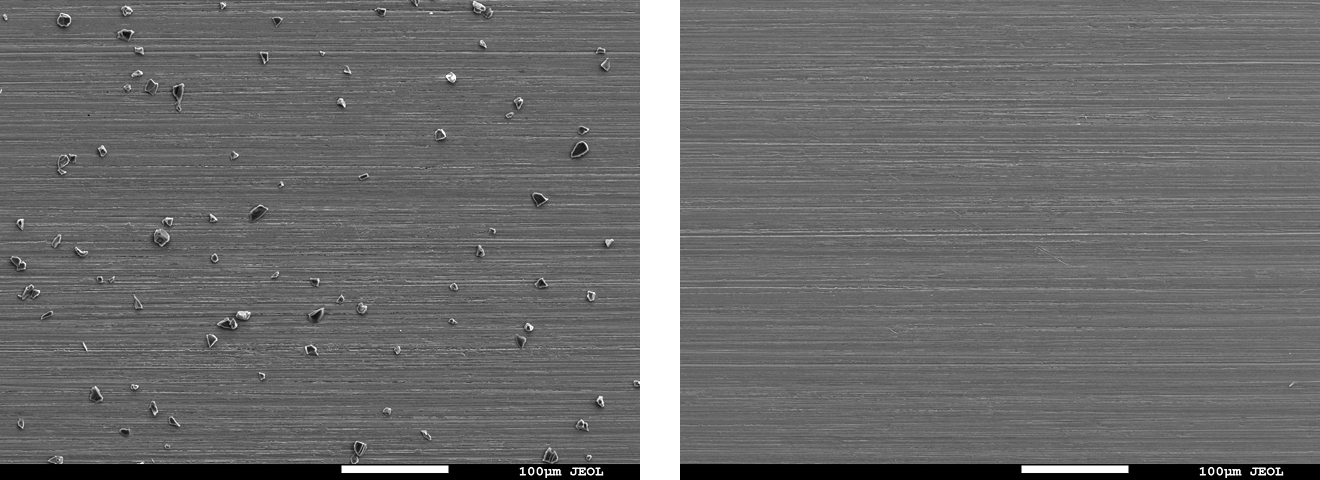
- As shown in Fig. 5, no residual oil film was observed
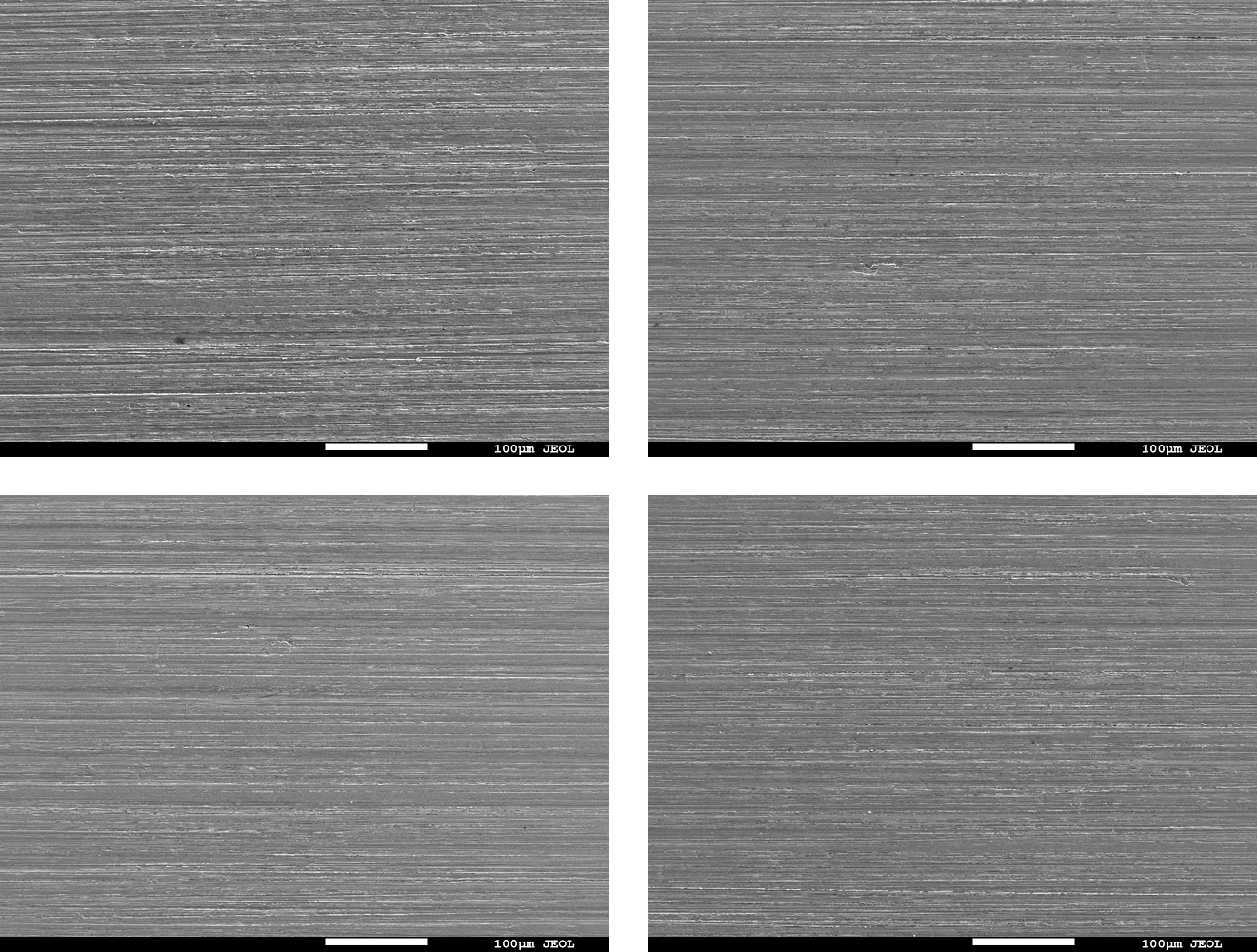
SEM observation and SEM-EDX analysis
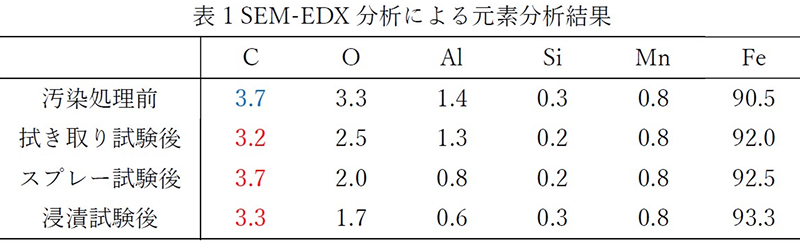
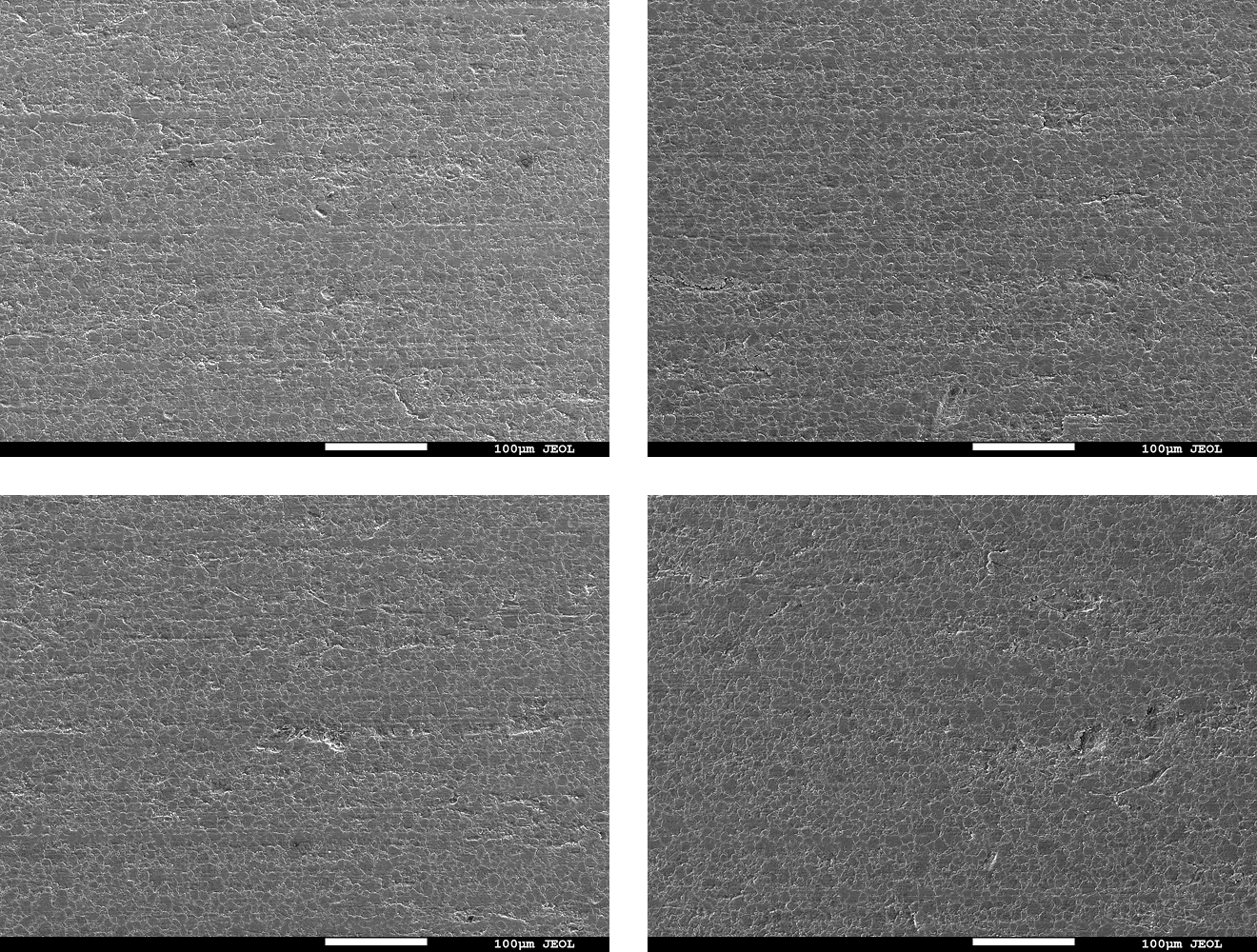
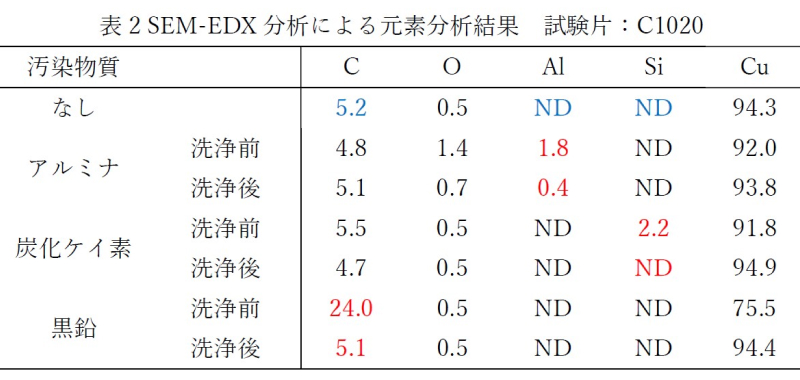
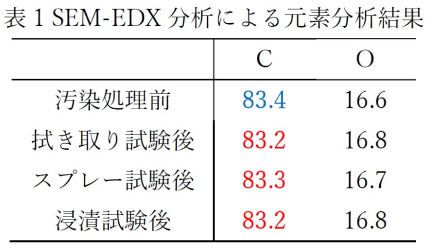
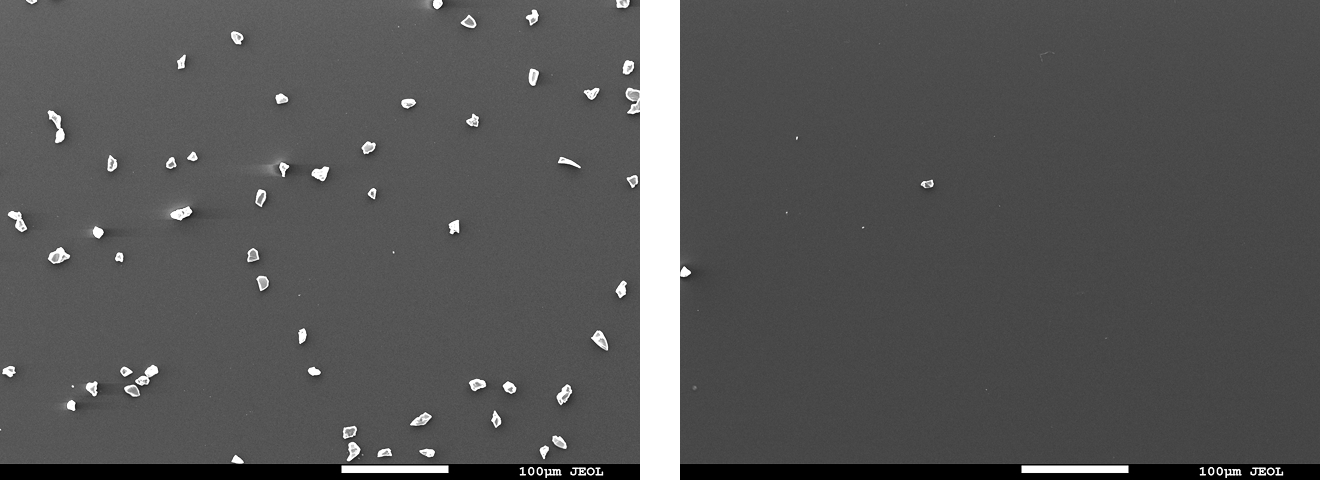
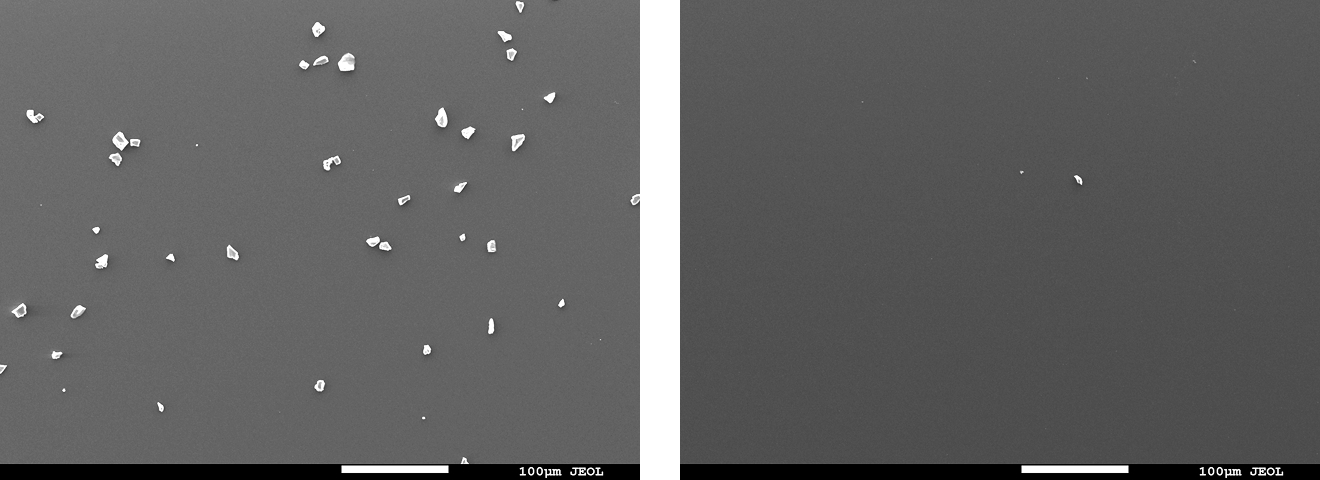
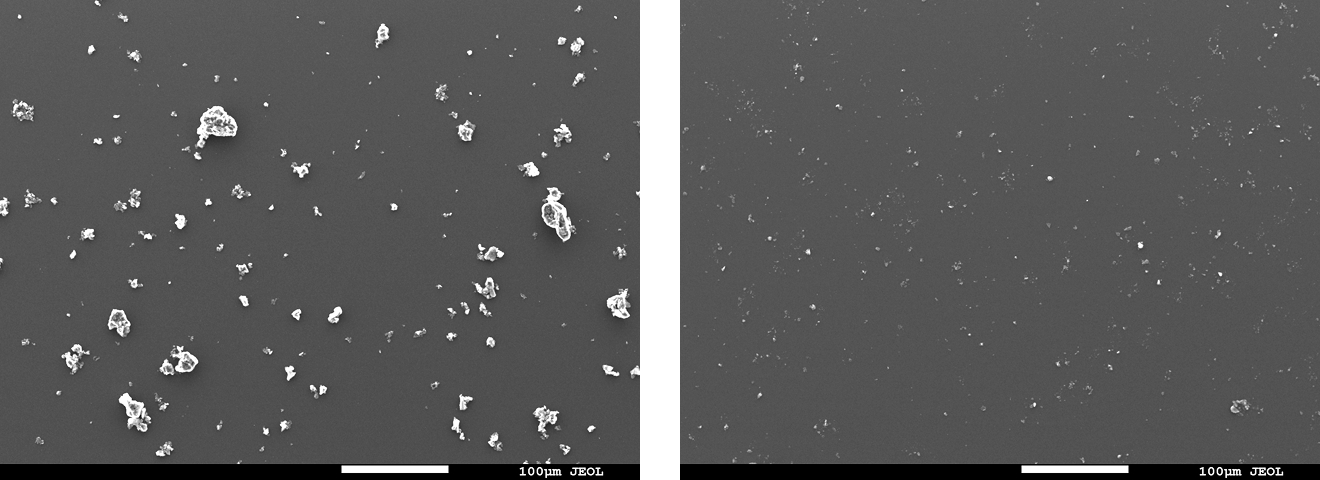
- Result: For all test methods, the post-cleaning specimen surfaces showed comparable appearance and carbon concentration in the elemental analysis results (Table 1) to those before contamination, suggesting that the contaminant was removed.
Test Site and Report Author
- Test site: Nagoya Municipal Industrial Research Institute, Materials Technology Dept.
- Test date:April 28, 2025

Fig. 1 Water-Soluble Cutting Oil
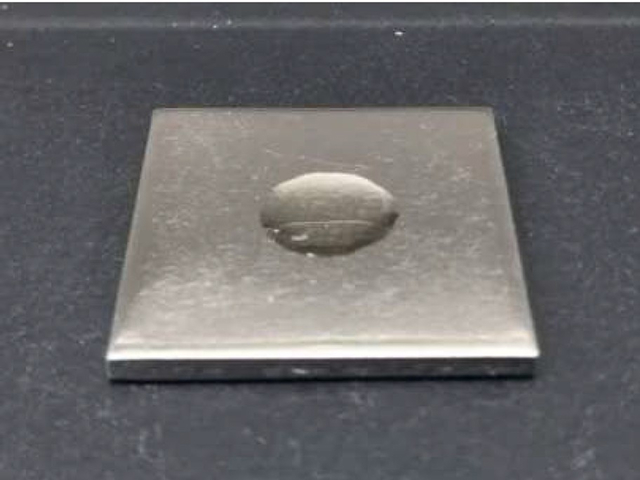

Fig. 2 Specimen Before Cleaning
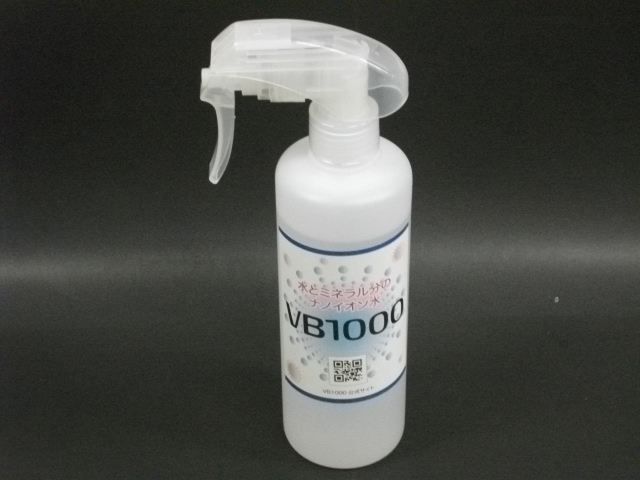

Fig. 3 Cleaning Solution (Spray Container)
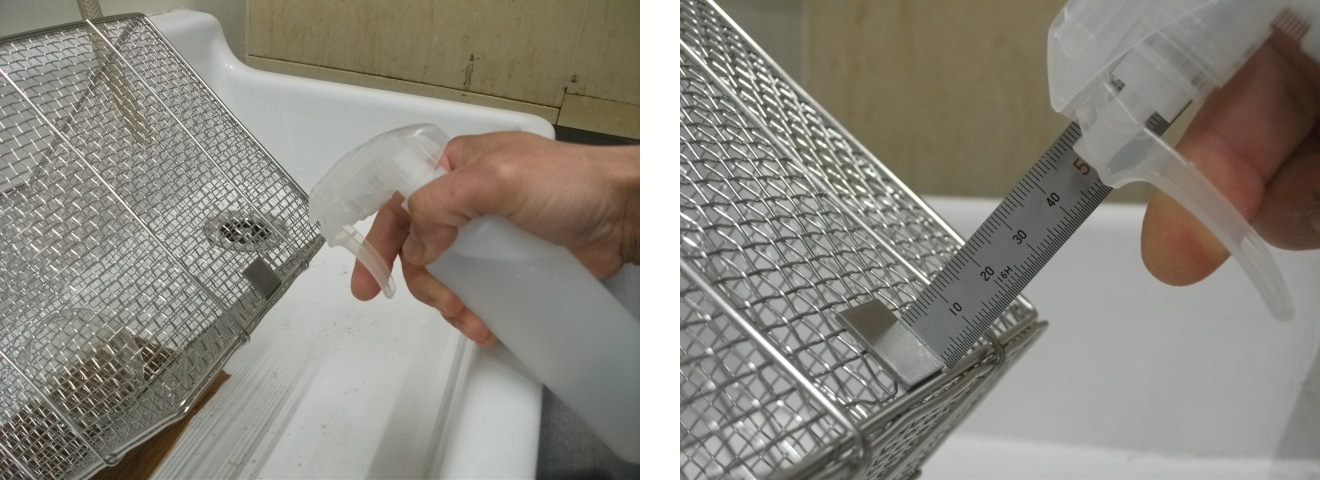

Fig. 4 Spraying Procedure
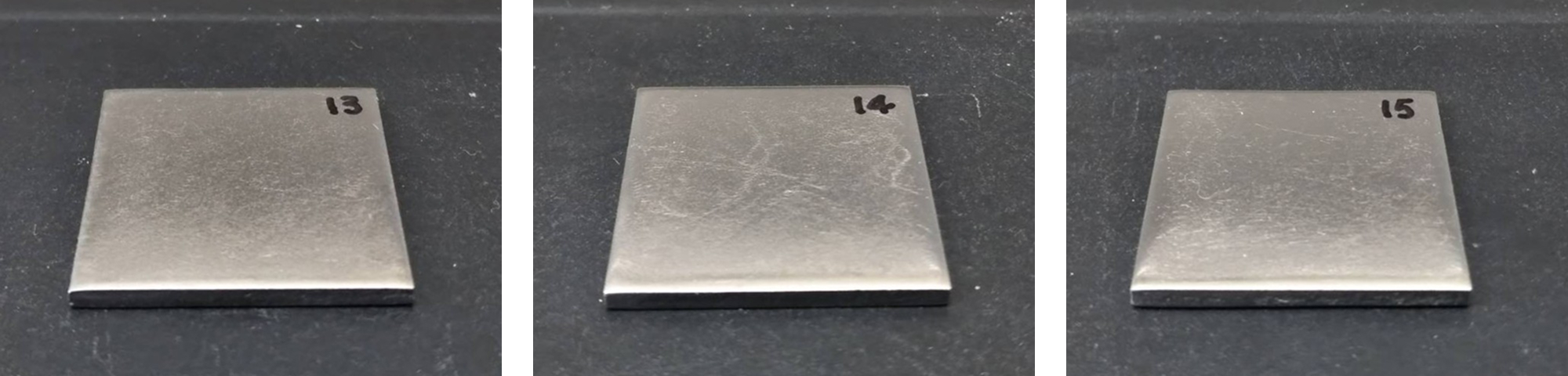

Fig. 5 Specimen After Cleaning
(Left: wipe / Center: spray / Right: immersion)
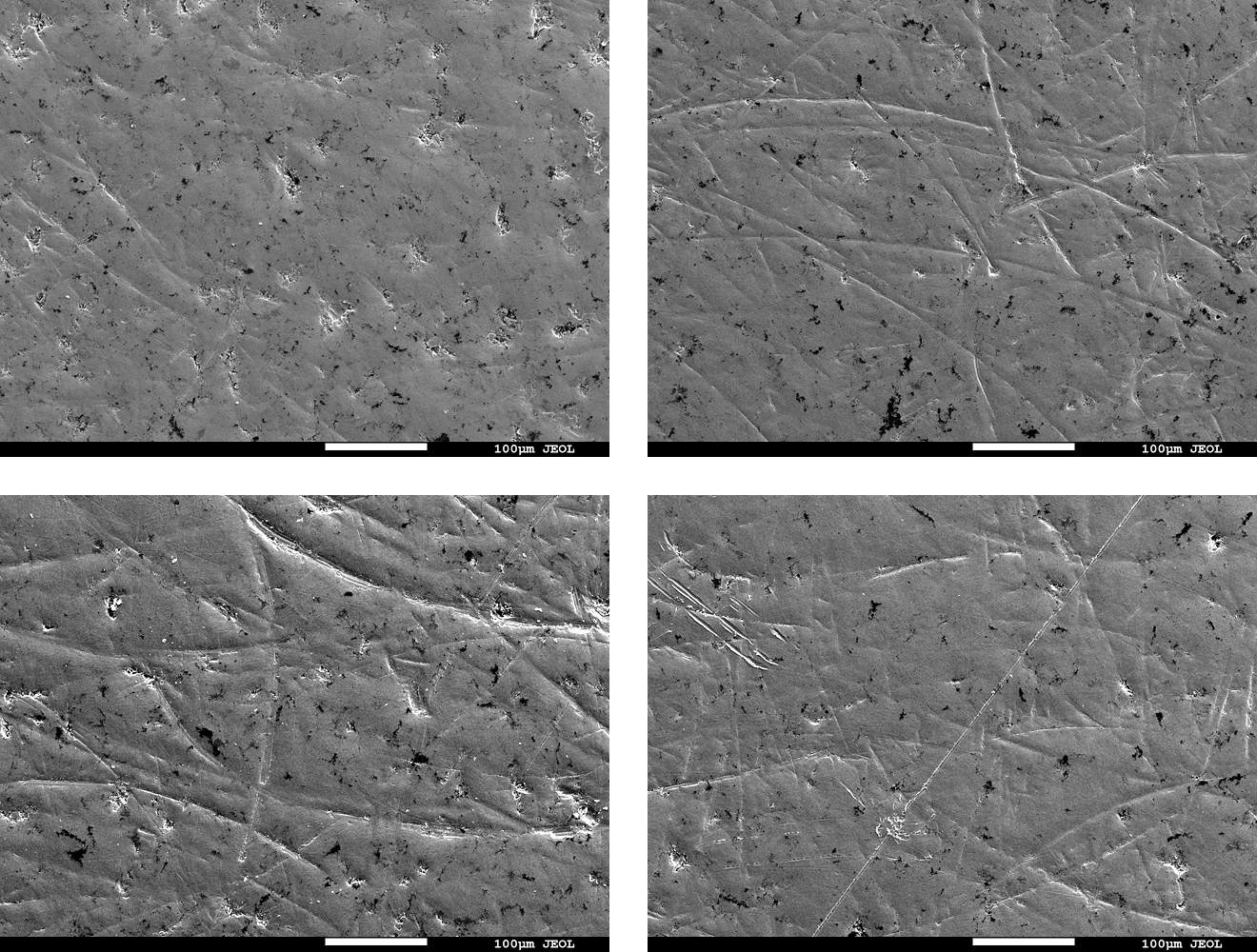
Fig. 6 Electron micrographs of the specimen surface before/after cleaning
(Top left:Before /Top right: wipe / Bottom left: spray / Bottom right: immersion)